FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS OF IMPRINTED GENES
Department: Physiology and Cancer
Research subject
For additional information, please visit Team website.
The Journot Lab is a multi-disciplinary lab that combines molecular biology, (stem) cell biology, genomics, and statistics to shed light on the biological functions of imprinted genes.Parental genomic imprinting is an epigenetic mechanism of gene regulation that restrains the expression of a gene to one allele depending on its parental origin. Genomic imprinting is essential for mammalian development. It targets ~150 genes in placental mammals (eutherians) and less than a dozen in marsupials (metatherians); it does not affect egg-laying mammals (prototherians) and other clades (birds, reptiles, amphibians, fishes…).
Imprinting defects at defined loci result in different syndromes with complex phenotypes : Silver-Russel, Angelman, Prader-Willi, Beckwith-Wiedemann, Temple, Kagami-Ogata, pseudohypoparathyroidism, and TNDM (Transient Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus). In addition, a number of imprinted genes are involved in tumor formation as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes.
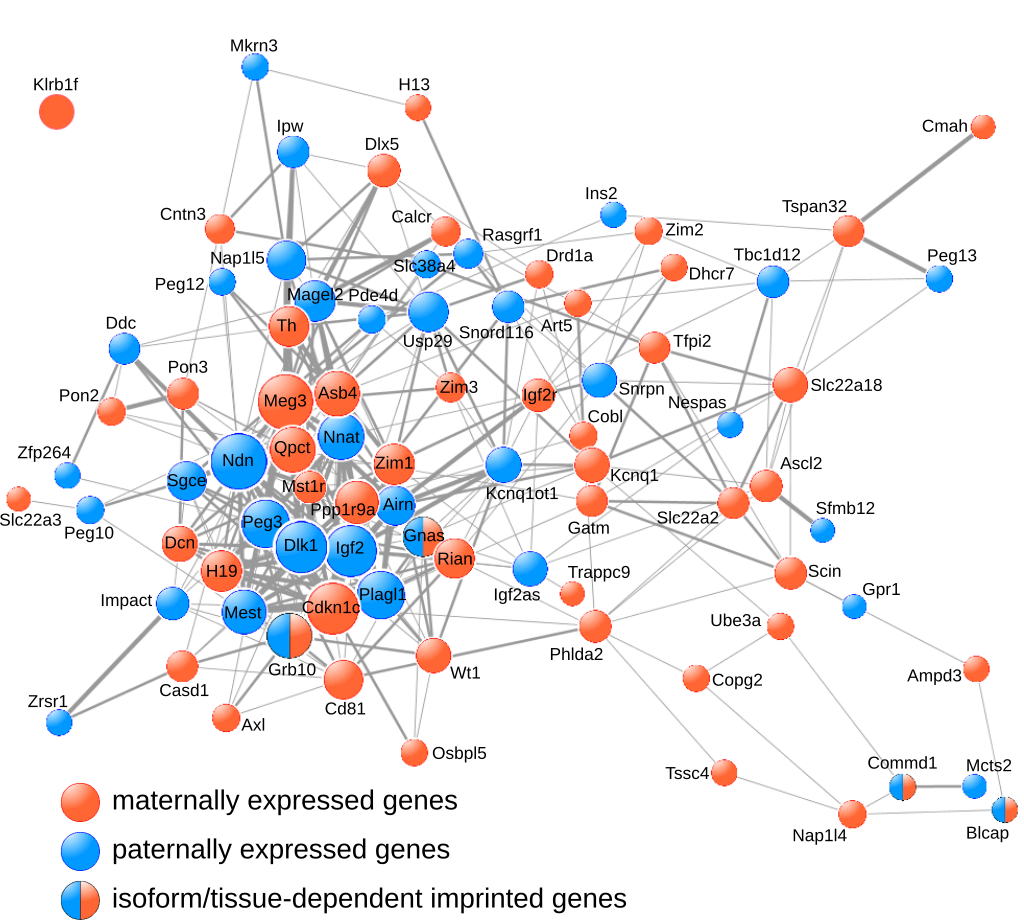
We showed that imprinted genes belong to a network of co-regulated genes we named the imprinted gene network (IGN; Varrault et al., Dev. Cell, 2006). We next found that the IGN is regulated at the transition from proliferation to quiescence and differentiation during fibroblast cell cycle withdrawal, adipogenesis in vitro, and muscle regeneration in vivo. The IGN also includes bi-allelically expressed genes, notably genes controling the composition of the extracellular matrix. Our observations suggest that imprinted genes are involved in a common biological process that may account for their seemingly diverse roles in embryonic development, obesity, diabetes, muscle physiology, and neoplasm (Al Adhami et al., Genome Res., 2015).
We are currently investigating the function of the IGN using different biological systems, together with systems-level and genome-wide approaches.
Legend to figure: Imprinted genes are frequently coexpressed.
The COXPRESdb meta-analysis of microarray data was searched for coexpression among murine imprinted geness.
The resulting coexpression links are represented using Cytoscape. Node size is proportional to node degree. Edge width represents the mutual rank between two given nodes.
Team
Team leader
Researchers
Technicians and engineers
Postdoctoral researchers and doctoral students
Major publications
- Reynès C, Kister G, Rohmer M, Bouschet T, Varrault A, Dubois E, Rialle S, Journot L, Sabatier R (2019) ISoLDE: a data-driven statistical method for the inference of allelic imbalance in datasets with reciprocal crosses. Bioinformatics. pii: btz564. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz564.
- Baudement MO, Cournac A, Court F, Seveno M, Parrinello H, Reynes C, Sabatier R, Bouschet T, Yi Z, Sallis S, Tancelin M, Rebouissou C, Cathala G, Lesne A, Mozziconacci J*, Journot L*, Forné T* (2018) High-salt-recovered sequences are associated with the active chromosomal compartment and with large ribonucleoprotein complexes including nuclear bodies. Genome Res. 28:1733-1746. doi: 10.1101/gr.237073.118.
- Varrault A, Dantec C, Le Digarcher A, Chotard L, Bilanges B, Parrinello H, Dubois E, Rialle S, Severac D, Bouschet T, Journot L (2017) Identification of Plagl1/Zac1 binding sites and target genes establishes its role in the regulation of extracellular matrix genes and the imprinted gene network. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:10466-10480. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx672.
- Bouschet T, Dubois E, Reynès C, Kota SK, Rialle S, Maupetit-Méhouas S, Pezet M, Le Digarcher A, Nidelet S, Demolombe V, Cavelier P, Meusnier C, Maurizy C, Sabatier R, Feil R, Arnaud P, Journot L, Varrault A (2017) In Vitro Corticogenesis from Embryonic Stem Cells Recapitulates the In Vivo Epigenetic Control of Imprinted Gene Expression. Cereb Cortex. 27:2418-2433. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhw102.
- Al Adhami H, Evano B, Le Digarcher A, Gueydan C, Dubois E, Parrinello H, Dantec C, Bouschet T, Varrault A, Journot L (2015) A systems-level approach to parental genomic imprinting: the imprinted gene network includes extracellular matrix genes and regulates cell cycle exit and differentiation. Genome Res. 25:353-67. doi: 10.1101/gr.175919.114.
- Varrault A, Eckardt S, Le Digarcher A, Sassetti I, Girard B, Meusnier C, Ripol C, Badalyan A, Bertaso F, McLaughlin J, Journot L, Bouschet T (2017) Mouse parthenogenetic embryonic stem cells with biparental-like expression of imprinted genes generate cortical-like neurons that integrate into the injured adult cerebral cortex. Stem Cells. in press