QUAND DEUX PROTÉINES IMPLIQUÉES DANS LE CANCER SE RENCONTRENT
QUAND DEUX PROTÉINES IMPLIQUÉES DANS LE CANCER SE RENCONTRENT : INTERACTIONS PHYSIQUES ET FONCTIONNELLES ENTRE LE RÉCEPTEUR ATYPIQUE DES CHIMIOKINES ACKR3 ET LA CONNEXINE 43, UNE PROTÉINE DES JONCTIONS GAP
Le récepteur atypique des chimiokines ACKR3 (précédemment appelé CXCR7) joue un rôle clé dans de nombreux processus biologiques comme la migration, la prolifération et la différenciation cellulaire, ainsi que dans de nombreux types de cancer, comme les gliomes. Les mécanismes de signalisation cellulaire à l’origine des effets physiopathologiques d’ACKR3 sont toutefois mal connus et ont fait l’objet de cette étude menée dans le cadre du consortium Oncornet par trois équipes de l’IGF (Equipes Marin, Mouillac et Lory) en collaboration avec des équipes des universités Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne, d’Amsterdam et de Jena, publiée dans Nature Communications le 25 Septembre 2020.
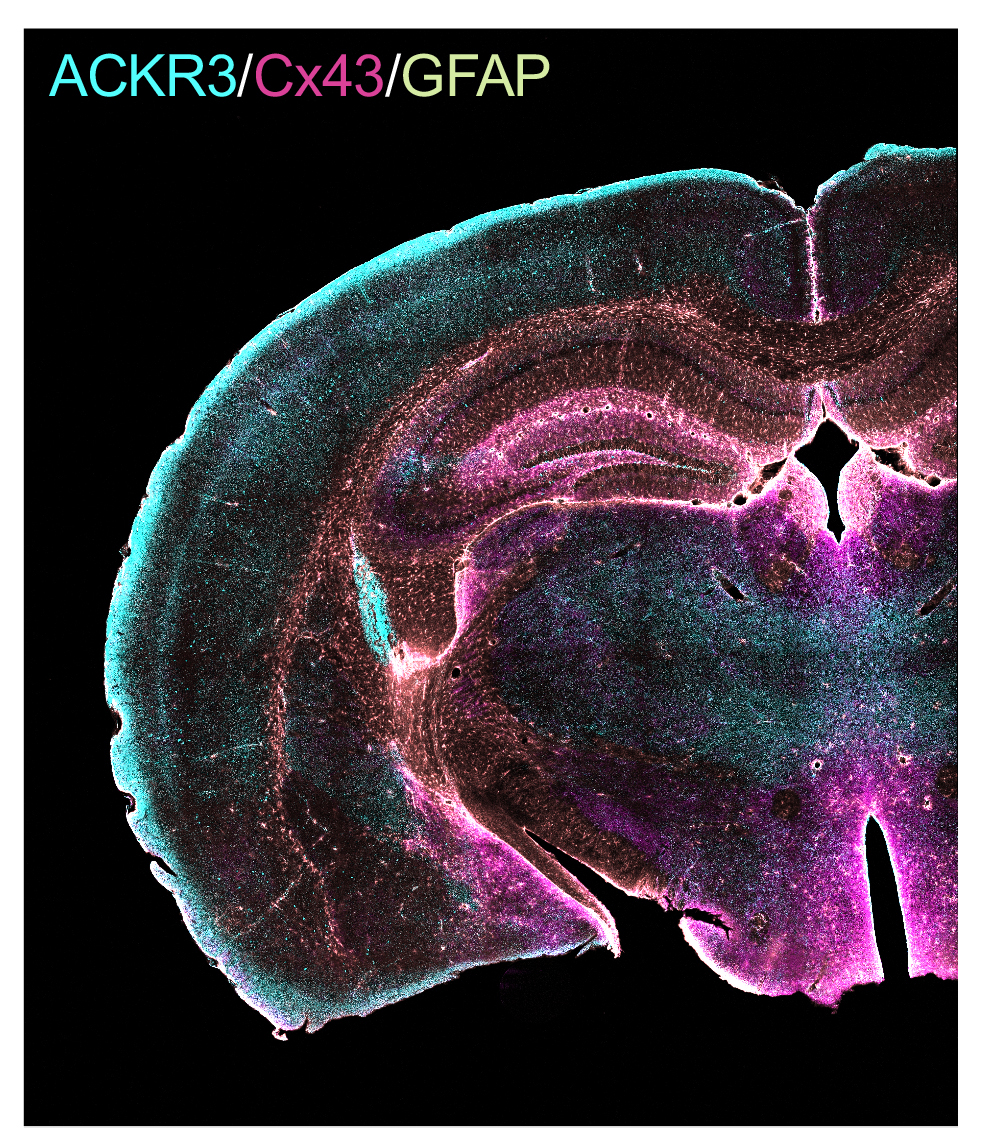
Un crible interactomique combinant la purification des partenaires du récepteur ACKR3 par affinité et leur identification par spectrométrie de masse (AP-MS) a d’abord permis d’identifier plus de 150 partenaires potentiels du récepteur. Ceux-ci incluent la connexine 43 (Cx43), une protéine des jonctions gap connue pour son implication dans la prolifération et le caractère invasif des gliomes. Du fait de l’implication conjointe des deux partenaires protéiques dans les gliomes, les liens fonctionnels entre les deux protéines ont fait l’objet d’une étude plus détaillée qui a d’abord établi qu’ACKR3 et la Cx43 forment un complexe dans le cerveau d’embryons de souris où les deux protéines sont co-exprimées dans les astrocytes entourant les capillaires cérébraux. De plus, des expériences de biochimie, de biologie cellulaire et d’électrophysiologie ont démontré que l’activation du récepteur inhibe le couplage jonctionnel impliquant la Cx43 dans les astrocytes via un mécanisme impliquant l’activation de protéines Gi/o et l’internalisation de la Cx43 dépendant de la b-arrestin2.
Cette étude apporte la première démonstration d’un lien physique et fonctionnel entre ACKR3 et la Cx43, mettant ainsi en lumière le rôle de l’interactome d’ACKR3 dans les effets physiopathologiques sous le contrôle de ce récepteur. Elle apporte également un élément de réponse à la question persistante du rôle des protéines G dans les effets de ce récepteur en suggérant une implication dépendant du type cellulaire.
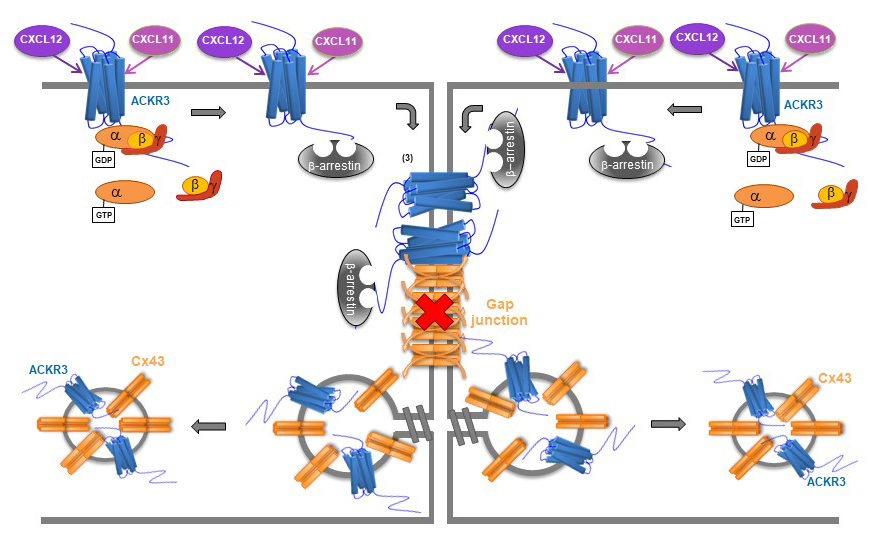 Représentation schématique du mécanisme d’inhibition du couplage jonctionnel impliquant la connexine 43 (Cx43) en réponse à l’activation du récepteur ACKR3 par la CXCL12 ou la CXCL11 dans les astrocytes.
Représentation schématique du mécanisme d’inhibition du couplage jonctionnel impliquant la connexine 43 (Cx43) en réponse à l’activation du récepteur ACKR3 par la CXCL12 ou la CXCL11 dans les astrocytes.
Ce mécanisme fait intervenir l’activation de protéines Gi/o et l’internalisation b-arrestine2–dépendante de la Cx43.
Nature Communications (2020)11:4855 . The atypical chemokine receptor 3 interacts with Connexin 43 inhibiting astrocytic gap junctional intercellular communication. Fumagalli A, Heuninck J, Pizzoccaro A, Moutin E, Koenen J, Séveno M, Durroux T, Junier MP, Schlecht-Louf G, Bachelerie F, Schütz D, Stumm R, Smit MJ, Guérineau NC, Chaumont-Dubel S, Marin P.
....................................................................................
WHEN TWO PROTEINS INVOLVED IN CANCER MEET: PHYSICAL AND FUNCTIONAL INTERACTIONS BETWEEN THE ATYPICAL CHEMOKINE RECEPTOR ACKR3 AND THE GAP JUNCTION PROTEIN CONNEXIN 43
The atypical chemokine receptor 3 (ACKR3, previously called CXCR7) is involved in key biological processes such as proliferation, migration and differentiation of various cells, and in the progression of numerous cancer types, including glioma. However, the intracellular pathways underlying ACKR3-dependent effects remain poorly characterized, an issue addressed in a Nature Communication paper published on September 25 2020 by three IGF teams (Marin, Mouillac, Lory) in frame of the ITN project Oncornet in collaboration with teams from University Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne University, VU University Amsterdam and Jena University.
An affinity purification coupled to mass spectrometry (AP-MS) interactomic screen first identified more than 150 candidate partners of ACKR3, including the gap junction protein connexin 43 (Cx43). In line with the joint influence of both ACKR3 and Cx43 in proliferation and invasiveness of glioma, the functional links between both proteins was then explored using a combination of biochemical, cell biology and electrophysiological experiments. The data show that ACKR3 and Cx43 form a complex in embryonic mouse brain where they are co-expressed in astrocytes surrounding blood vessels. Furthermore, agonist stimulation of ACKR3 inhibits Cx43-mediated gap junctional intercellular communication in astrocytes through a mechanism involving Gi/o protein activation and b-arrestin-2-dependent Cx43 internalization.
This study provides the first demonstration for a physical and functional link between the CXCL11/CXCL12/ACKR3 axis and Cx43 and highlights the key role played by ACKR3 interactome in determining the functional outcome of this chemokine receptor engaged in a broad range of pathologic conditions such as cancers. It also provides new insight into the persistent conundrum of the role of G proteins in ACKR3 pathophysiological effects by suggesting a cell type-dependent involvement of G proteins.
 Schema illustrating the inhibition of connexin 43 (Cx43) gap junctional intercellular communication upon activation of ACKR3 by CXCL12 or CXCL11 in astrocytes.
Schema illustrating the inhibition of connexin 43 (Cx43) gap junctional intercellular communication upon activation of ACKR3 by CXCL12 or CXCL11 in astrocytes.
This effect involves activation of Gi/o proteins and b-arrestin2-dependent Cx43 internalization.
Nature Communications (2020)11:4855 . The atypical chemokine receptor 3 interacts with Connexin 43 inhibiting astrocytic gap junctional intercellular communication. Fumagalli A, Heuninck J, Pizzoccaro A, Moutin E, Koenen J, Séveno M, Durroux T, Junier MP, Schlecht-Louf G, Bachelerie F, Schütz D, Stumm R, Smit MJ, Guérineau NC, Chaumont-Dubel S, Marin P.