AMORÇAGE DES RÉCEPTEURS AUX GLUCOCORTICOÏDES DANS LA MALADIE D’ALZHEIMER
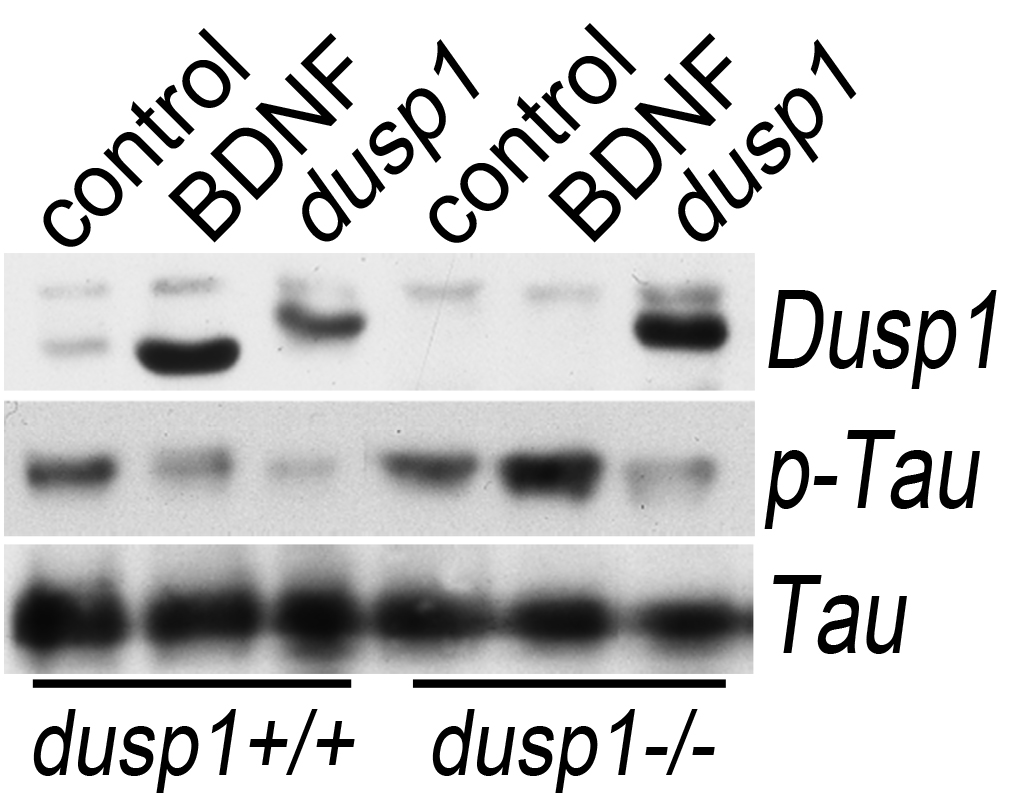
Les équipes Jeanneteau et Parmentier étudient la phosphatase dusp1 comme suppresseur endogène de la neuropathologie de TAU. La neurotrophine BDNF utilise le récepteur aux glucocorticoïdes comme effecteur de signalisation pour exprimer dusp1 dans le cerveau. La délétion de cette voie de signalisation dans le cerveau de souris conduit à la phosphorylation ectopique d’une forme pathologique de TAU. Ce défaut est retrouvé dans le cerveau de patients souffrant de la maladie d’Alzheimer.
Citation: Margarita Arango-Lievano, Camille Peguet, Matthias Catteau, Marie-Laure Parmentier, Synphen Wu, Moses Chao, Stephen Ginsberg, Freddy Jeanneteau
Deletion of Neurotrophin Signaling through the Glucocorticoid Receptor Pathway Causes Tau Neuropathology. Sci Reports, 2016
PRIMING GLUCOCORTICOID RECEPTORS AGAINST ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
The Jeanneteau and Parmentier Labs investigated the phosphatase dusp1 as suppressor of TAU neuropathology. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor uses the glucocorticoid receptor as signaling effector to express dusp1 in brain. Deletion of this pathway caused ectopic TAU phosphorylation and synaptic loss in mouse cortex. Expression of dusp1 is abnormally low in brains of subjects affected with Alzheimer’s disease.
Citation: Margarita Arango-Lievano, Camille Peguet, Matthias Catteau, Marie-Laure Parmentier, Synphen Wu, Moses Chao, Stephen Ginsberg, Freddy Jeanneteau
Deletion of Neurotrophin Signaling through the Glucocorticoid Receptor Pathway Causes Tau Neuropathology. Sci Reports, 2016